44 egg structure with labels
Structure of the Amniotic Egg - Memorial University of Newfoundland the arrangement of membranes in a typical egg-laying oviparousvertebrates. In live-bearing viviparousvertebrates, the shell and chorionic membrane are absent and the allantoic and yolk sac membranes are incorporated into the connection with the maternal circulation. Figure ©1999 Campbell et al.; text © 2005 by Steven M. Carr Structure of the Gametes - Developmental Biology - NCBI Bookshelf Flagella are complex structures. The major motor portion of the flagellum is called the axoneme. It is formed by microtubules emanating from the centriole at the base of the sperm nucleus ( Figures 7.2 and 7.3 ). The core of the axoneme consists of two central microtubules surrounded by a row of nine doublet microtubules.
Illustrating the Layers of the Earth Through Egg Dissection The Earth is divided into three layers: the crust, the mantle and the core. The mantle and the core are further divided into an inner and outer layer. This simple activity requiring only boiled eggs models the 3 layers of the Earth. It is most appropriate for elementary students but can be utilized with variations (See below) for middle school ...

Egg structure with labels
Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Science of Cooking 1. Eggshell The outer eggshell is made almost entirely of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and is covered with as many as 17,000 tiny pores. It is a semipermeable membrane, which allows air and moisture to pass through its pores. The shell also has a thin outermost coating called the bloom or cuticle that helps keep out bacteria and dust (see below 15). What Do the Labels on Egg Cartons Actually Mean - Lifehacker It probably matters in finicky recipes.". Grade AA, grade A, grade B - Grading measures egg "quality" according to the USDA. Eggs are downgraded for having air cells, blood spots, or ... Clean Label Soups & Sauces Solutions | Ulrick & Short We have over 20 years of food industry knowledge and expertise in clean label ingredient development. We work with manufacturers like you to overcome the most difficult product formulation challenges from reducing fat and sugar, replacing egg and removing phosphates to improving product stability, texture and appearance.
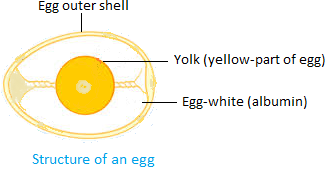
Egg structure with labels. The Parts of the Egg - Virginia Tech In a fresh egg, we can see white cords attached to the yolk sac. These two cords, called chalazae, are made of twisted strands of mucin fibers that are a special form of protein. The chalazae hold the yolk in the center of the egg. The yolk is the source of food for the embryo and contains all the fat in the egg. Structure of the Egg - Incubation and Embryology - University of ... The egg is a biological structure intended by nature for reproduction. It protects and provides a complete diet for the developing embryo, and serves as the principal source of food for the first few days of the chick's life. The egg is also one of the most nutritious and versatile of human foods. Egg Labels Explained - Cornucopia Institute Apr 17, 2017 · Egg Grades: A, AA, or B The USDA grades eggs AA, A, or B, with AA being the best, most uniform egg and B the most unsightly or somehow defective. Critics argue that the grades are cosmetic because they don’t promise protection from salmonella, the most dangerous and common pathogen carried by eggs. egg box labels - egg box labels on sale - qualitydress.com All Verified egg box labels suppliers & egg box labels manufacturers have passed our Business License Check, they can provide quality egg box labels products. ...your own packaging for your company. 3) The box could be customized according to your design.
Types of Eggs - The Spruce Eats What Egg Labels Mean Conventional eggs are typically just labeled "Eggs," but there are a few designations that you might also see on egg labels. 2 Cage-free: Cage-free eggs come from hens that are free to walk around the hen house, as opposed to conventional eggs, which come from hens that are kept in small cages. Label the following structure: (Figure 2) Unripe | Chegg.com Biology questions and answers. Label the following structure: (Figure 2) Unripe tomato epidermal cells, locate the chloroplasts and chlorophylls in the figure below. Use arrows and label them accordingly. The Different Parts of an Egg | Sauder's Eggs Jun 13, 2018 · Shell Size: In the United States, egg cartons are graded and sold based on their weight per dozen. Eggs can be categorized into seven volumes, with jumbo and large eggs the highest commercially sold and most referenced throughout recipes. An egg’s weight also includes the net mass of the entire makeup, including its shell. Egg: Definition, Structure and Classification - Your Article Library When eggs are freshly laid, the shell is covered with a substance called 'bloom' that gives it a feeling much like that of a thin lime coating deposited in a pan after water boils. This coating disappears gradually as the egg is exposed to air, but as long as it remains, the egg may be considered as fresh and germ-proof.
Label Chicken Egg (#1) Printout - EnchantedLearning.com Label the Chicken Egg (#1) Label the cross section of a newly-laid chicken egg. Chickens Bird Printouts air cell - an empty space located at the large end of the egg; it is between the inner and outer shell membranes. chalaza - a spiral, rope-like strand that anchors the yolk in the thick egg white. Science of Eggs: Anatomy of an Egg | Exploratorium An air space forms when the contents of the egg cool and contract after the egg is laid. The air cell usually rests between the outer and inner membranes at the egg's larger end, and it accounts for the crater you often see at the end of a hard-cooked egg. The air cell grows larger as an egg ages. The egg white is known as the albumen, which ... Clean Label Egg Replacement - Ulrick & Short We have over 20 years of food industry knowledge and expertise in clean label ingredient development. We work with manufacturers like you to overcome the most difficult product formulation challenges from reducing fat and sugar, replacing egg and removing phosphates to improving product stability, texture and appearance. Egg - Wikipedia An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal that can survive on its own, at which point it hatches.. Most arthropods, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not.
Egg labels - the complete guide; how to understand them - AgronoMag This category of eggs is labeled with 1 in the EU. Chickens grown in this system spend the day out, each with a space of at least four square feet, and during night they retreat to enclosed spaces. They are also provided with hay for hay nesting and for laying eggs. However, their food is not certified as organic.
Structure of the egg - HEDEGAARD - DAVA The structure of the egg An egg basically consists of three parts: a shell an egg white an egg yolk An egg from a hen consists of approximately 2/3 egg white and 1/3 egg yolk. The eggshell The shell is built of 8-10,000 pores, which ensures that oxygen can penetrate and CO 2 and other gases can escape.
PDF STRUCTURE OF A BIRD'S EGG Name Label the parts of the newly fertilized ... STRUCTURE OF A BIRD'S EGG Name Label the parts of the newly fertilized bird's egg and the developing bird's egg in the diagrams below. State the purpose/function of each part.
label parts of a cell yolk is surruondedby the substance called - Science - Cell - Structure we have 9 Images about yolk is surruondedby the substance called - Science - Cell - Structure like Parts and Function of Digestive System for Med School & Nursing, 2.4.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes - YouTube and also Connective tissue - BIOLOGY4ISC.
Understanding Egg Labels - Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics The color of the eggshell relates to the breed of chicken. Chickens with white feathers and white earlobes typically lay white eggs. In contrast, brown eggs are laid by birds with reddish-brown feathers and red earlobes. Did you know that there are even chickens that lay shells that are blue and speckled? Though they tend to cost more, the nutritio...
Aeration/Foaming/Structure - American Egg Board Aeration can be achieved in several ways including biological (yeast), chemical (baking soda), mechanical (methods of mixing certain ingredients or the batter through whipping or beating), physical (lamination or steam), or a combination of those methods. Each is designed to introduce a gas, such as air, into a liquid or viscous solution. 1.
Chicken egg structure ( in simple way) - YouTube In this video I have explained about chicken egg structure in a simple way.. Thank uhttps:// ...
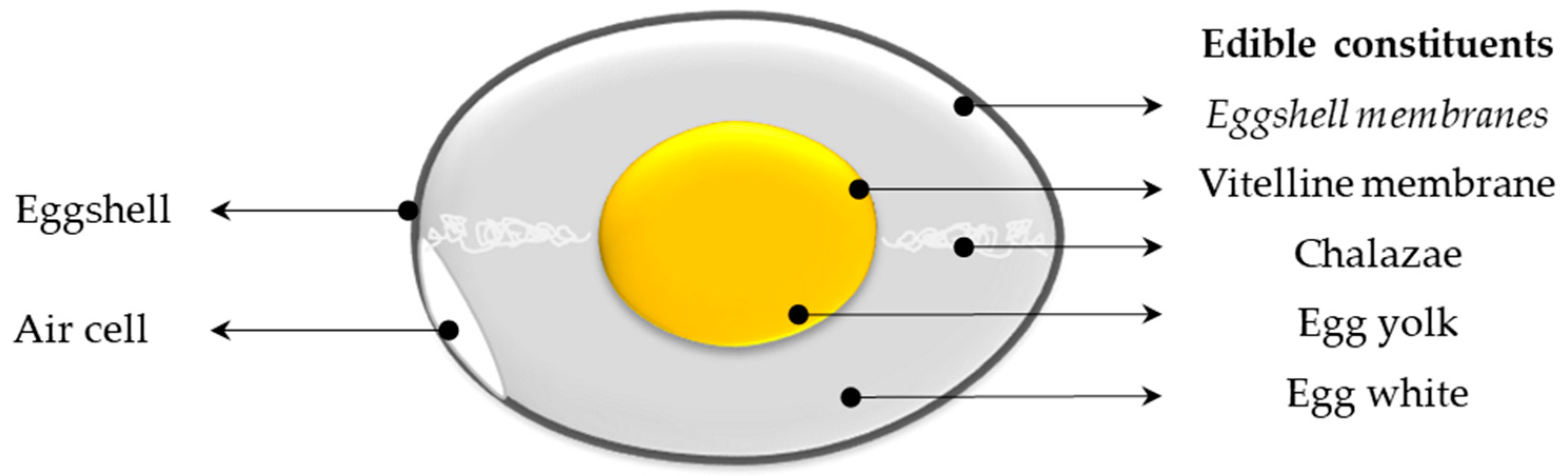
PDF Egg Parts - University of Illinois Extension Color each part of the egg a different color and label each part of the egg. Use each word only once: air cell germinal disc vitelline membrane albumen or white membranes yolk chalaza shell albumen or white shell KEY air cell yolk chalaza vitelline membrane membranes germinal disc. Title: Embryology Worksheets Author: OUP
Physical Structure and Composition of an Egg - Prezi Chalaza. This is the ropey strands of egg white at both sides of the egg, which anchor the yolk in place in the center of the thick white. Accounts for most of an egg's liquid weight, about 67%. This is produced by the oviduct and consists of four alternating layers of thick and thin consistencies.
The Anatomy of an Egg: We Take a Closer Look - Hobby Farms The albumen is packed with protein—about 40 proteins, actually—while the rest is water. It includes four sections: the outer thin, the outer thick, the inner thin and the inner thick. The albumen connects to the yolk and shell with two cords called chalazae.
Label the diagram of an antibody structure. Light | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Label the diagram of an antibody structure. Light chain Heavy chain Fab fragment Constant region includes Fc fragment Variable region Antigen-binding sites E Light chain Heavy chain Fab fragment Constant region includes Fc fragment Variable region Antigen-binding sites E
The Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Parts and Functions of an Egg An eggshell is a semipermeable membrane, allowing air and moisture to pass the pores. Bloom or Cuticle It is a thin outermost coating of the eggshell which keeps out dust and bacteria. It keeps out the dust by sealing the pores on the eggshell. This also reduces moisture loss from the interior of the egg. Outer and inner shell membranes
Clean Label Soups & Sauces Solutions | Ulrick & Short We have over 20 years of food industry knowledge and expertise in clean label ingredient development. We work with manufacturers like you to overcome the most difficult product formulation challenges from reducing fat and sugar, replacing egg and removing phosphates to improving product stability, texture and appearance.
What Do the Labels on Egg Cartons Actually Mean - Lifehacker It probably matters in finicky recipes.". Grade AA, grade A, grade B - Grading measures egg "quality" according to the USDA. Eggs are downgraded for having air cells, blood spots, or ...
Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Science of Cooking 1. Eggshell The outer eggshell is made almost entirely of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and is covered with as many as 17,000 tiny pores. It is a semipermeable membrane, which allows air and moisture to pass through its pores. The shell also has a thin outermost coating called the bloom or cuticle that helps keep out bacteria and dust (see below 15).









Post a Comment for "44 egg structure with labels"